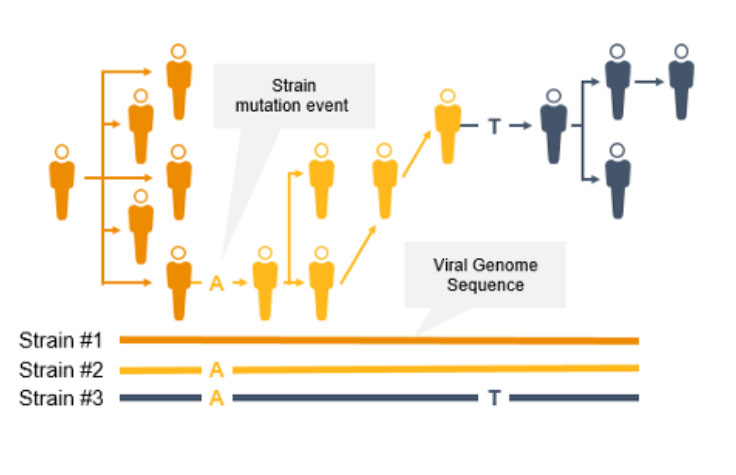
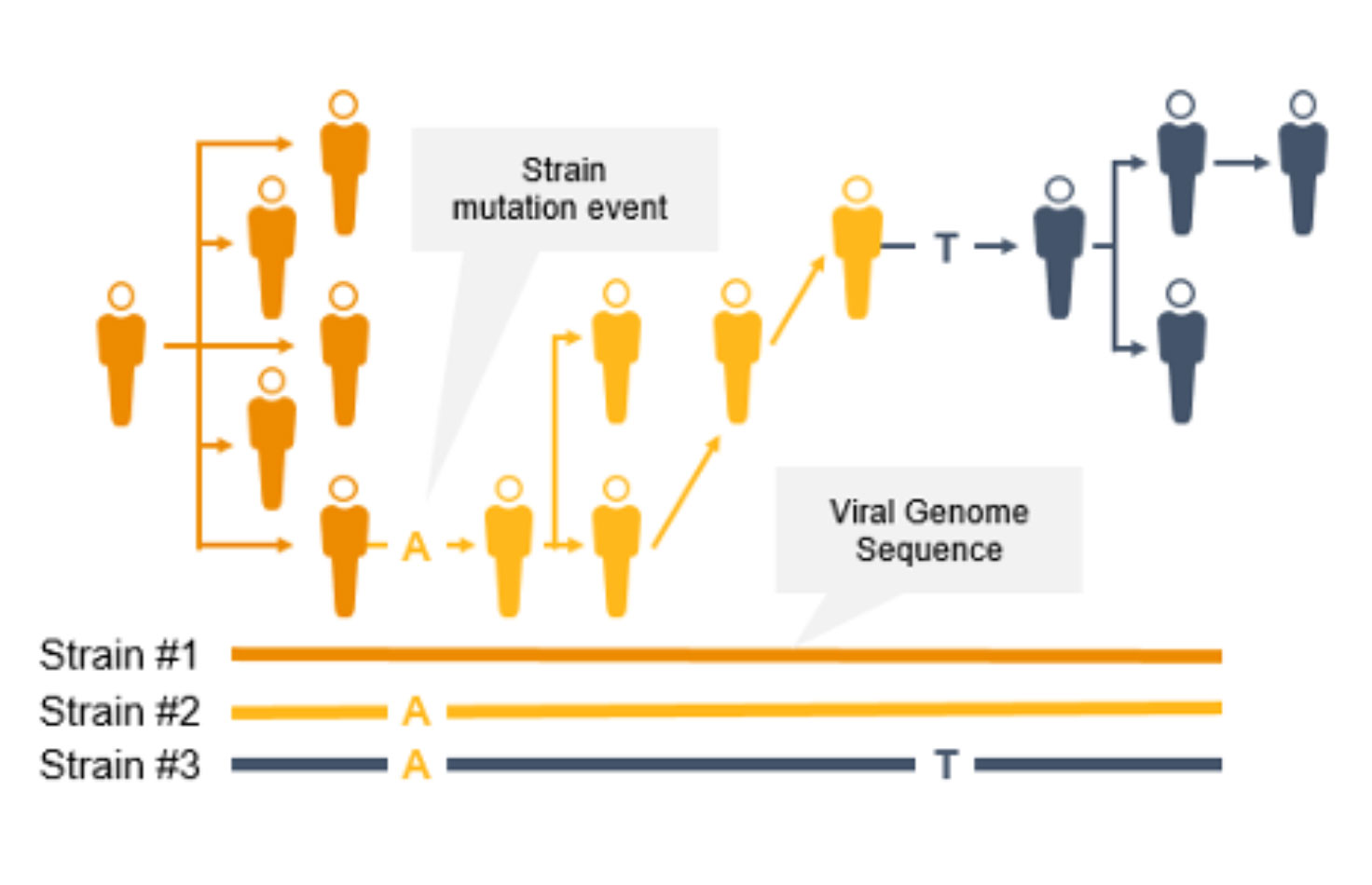
传染病的基因组监测

识别和追踪传染性疾病威胁
使用NGS进行基因组学监测可追踪传染性疾病传播,鉴定冠状病毒新毒株和其他新出现的病原体。利用几乎完整的病原体基因组测序数据,我们可以实施有效的传染性疾病监测策略,预防进一步的传播和感染。
利用新一代测序(NGS)进行传染性疾病监测可以:
- 跟踪传染性疾病在全球的传播途径
- 确定确定冠状病毒等病原体在传播过程中的突变速率
- 鉴定病原体中的新型和已知突变,如冠状病毒、甲型流感和乙型流感等
- 研究传染性疾病治疗耐受性
- 研究疫苗逃逸机制
基因组学监测有助于公共卫生人员追踪疫情路径,了解传播途径,确定病原体进化的速度以及病原体当下的变化是否会影响诊断效果或治疗效果。
监测和鉴定冠状病毒突变
随着冠状病毒的突变,新毒株不断进化,例如B.1.1.7(英国)、B.1.351(南非)和B.1. 426(加利福尼亚)。监测和监控极为重要,因为突变可能导致更强的传播性或传染性。这些冠状病毒突变可能会降低疫苗的有效性/保护性,甚至逃避检测诊断。
NGS是一种重要的传染性疾病监测技术。与PCR技术不同,NGS不仅能追踪冠状病毒突变毒株的传播,还能鉴定新型冠状病毒突变。利用NGS,科学家可以从样本中检测到低频次要变异、多种多态性以及新型突变。
流行病学家可使用NGS全基因组菌株分型快速识别并鉴定突变,以防止进一步传播。菌株水平的追踪可支持爆发聚集地和传播途径的识别。
相反,PCR旨在检测病原体基因组特定区域的存在,不会在这些快速进化的病原体基因组中识别出新的突变。此外,如果引物或探针结合区域发生突变,PCR的性能可能会受到影响。
An Outbreak Anywhere Can Become an Outbreak Everywhere
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is a large, double-stranded DNA virus first identified in 1958. Historically, the monkeypox virus has caused sporadic human outbreaks in central and west Africa, with a mortality rate between 1% and 10%[1]. In the spring of 2022, outbreaks were observed in non-endemic countries of Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia. Public health surveillance efforts are underway in these countries to prevent the further spread of the monkeypox virus.
NGS is a valuable technology for genomic surveillance of infectious diseases such as monkeypox. Not only can NGS track the prevalence of mutant strains, but it can also identify novel mutations. As a result, scientists can now employ NGS-based technologies to detect low-frequency minority variants, multiple polymorphisms, and novel variants with speed and accuracy in a high-throughput format. These factors are vital in helping epidemiologists identify and characterize outbreak clusters, transmission routes, and mutations to prevent further spread.
Illumina is proud to have supported the global expansion of NGS capacity and capabilities for public health during the COVID pandemic. These resources can now be used for the surveillance of pathogens such as monkeypox virus, ebola virus, mycobacterium tuberculosis, and many others.
Compare NGS Pathogen Surveillance Methods
| Testing Needs | Amplicon | Target Enrichment | Shotgun Metagenomics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed & Turnaround Time | |||
| Scalable & Cost-Effective | |||
| Identify Novel Pathogens | |||
| Track Transmission | |||
| Detect Mutations | |||
| Identify Co-Infections & Complex Disease | |||
| Detect Antimicrobial Resistance |
Adequately meets laboratory testing needs
Partially meets laboratory testing needs
More About Infectious Disease Surveillance Sequencing Methods
Amplicon Sequencing
Detect and fully characterize a known virus. Whole genome sequencing via an amplicon approach is ideal for known viruses with small genomes. This method involves analyzing genomic regions of interest with ultra-deep sequencing of PCR amplicons.
Target Enrichment Sequencing
Detect and characterize coronaviruses, flu viruses, and other pathogenic organisms, as well as associated antimicrobial resistance alleles. These insights can help public health officials monitor outbreaks and optimize infection control strategies. This method captures genomic regions of interest via hybridization to target-specific probes.
Shotgun Metagenomics
Comprehensively sequence all organisms in a given sample and identify novel, or emerging pathogens such as mokeypox virus. This NGS method can help accelerate outbreak investigations and support development of new laboratory tests.
Surveillance of Infectious Disease through Wastewater Sequencing
Learn how to use wastewater sequencing to monitor SARS-CoV-2 variants and other respiratory viruses in the community.
Read Application Note冠状病毒基因组学监测工作流程
特色产品

NovaSeq Reagent Kits
适用于NovaSeq 6000系统的试剂套件提供了随时可用的试剂盒,可用来进行簇生成与边合成边测序。

NextSeq 550系统
灵活的NextSeq 550系统可实现高通量测序和芯片扫描之间的无缝过渡。

NextSeq 2000
能助您探索一系列现有及新兴应用,突破效率,突破极限的开创性台式测序仪。
Podcast: Genomic Surveillance & Testing for SARS-CoV-2
Christopher Mason from Weill Cornell Medicine describes his multifaceted approach to the urgent need for COVID-19 testing and surveillance. He also discusses his recent Nature paper involving use of omics methods to study COVID-19 host responses and drug interactions.
预防下一次大流行
据估计,多达75%的新型或新出现的传染性疾病具有人畜共患疾病传染源。1,2 我们现在知道,人畜共患疾病宿主在病原体传播中起着重要作用。有了NGS,人们能够筛查蝙蝠等宿主动物,以预测和预防病毒病原体的爆发。
利用基于NGS的靶向富集或宏基因组学进行传染性疾病监测可帮助我们了解跨物种传播、人畜共患传染性疾病出现方式、传播和对常见疗法产生耐受性,并使我们能够更好地控制、治疗和预防疾病爆发。
靶向富集测序可放大至监测人畜共患疾病病原体,而宏基因组学基因组监测支持对多种病原体进行无偏差、无培养的检测和鉴定。宏基因组学还能帮助我们了解微生物组和病原体相互作用之间的关系,这对于控制传染性疾病措施的制定十分重要。
了解详情:
靶向富集宏基因组学测序
更多传染性疾病监测应用
食品监测
微生物全基因组测序可评估从食品传播到人类的病原体的全部遗传变异信息。我们能识别的变异越多,找到感染源和传播途径的可能性越高。
病毒监测
靶向富集使用杂交捕获目标基因组区域。此方法可提供检测病毒所需的高灵敏度,并提供病毒传播和进化的相关信息。
呼吸道感染监测
这些panel可提供呼吸道病原体和呼吸道病毒检测和鉴定的靶向富集测序解决方案,包括COVID和流感。
人畜共患疾病宿主监测
鸟枪法宏基因组学能够对人畜共患疾病样本中来自完整微生物群落的DNA进行测序,包括新型物种和已知物种。这些测序read可用于了解AMR基因的出现、进化和传播及物种分布。
医院获得性感染监测
基于NGS的细菌基因组测序结合用户友好的bioMérieux软件,可进行全面的分离株区分和鉴定。
Frequently Purchased Together
特色基因组监测文献
污水基因组测序检测区域性流行SARS-CoV-2变异株
为了及早检出新出现的菌株需要进行大规模基因组监测
通过监测和基于探针捕获的NGS发现蝙蝠冠状病毒
相关解决方案
冠状病毒测序
使用NGS鉴定新型冠状病毒毒株和其他病原体,无需事先了解该生物体。
冠状病毒软件
检测和鉴定病毒序列、检测COVID-19宿主反应、并将发现提交到共享数据库的软件工具。
COVID-19宿主风险与宿主反应
研究宿主遗传变异并分析驱动免疫应答的分子机制的方法。
参考文献
- Woolhouse ME, Gowtage-Sequeria S. Host range and emerging and reemerging pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1842–7. 10.3201/eid1112.050997
- Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, et al. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature. 2008;451:990–3.